Continue on Phone Android Wear Update
Wear OS apps run directly on a watch, giving you access to hardware such as sensors and the GPU. Wearable apps are similar to other apps that use the Android SDK, but differ in design and functionality.
A Wear OS app should work independently of a phone app, allowing users the greatest flexibility in their choice of phones. For more information, see Standalone versus non-standalone Wear OS apps.
Note: You can test your app on an actual watch using USB, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth as described in Debug a Wear OS app. Debugging your app on an actual watch enables you to better evaluate the total user experience. You can also use the watch emulator in Android Studio to test your app with different screen shapes and sizes.
Set up your environment
Install the latest version of Android Studio. For information about creating apps in Android Studio, see Projects overview.
Use the SDK manager to confirm that you have the latest version of the Android platform that supports Wear OS, Android 11 (API level 30).
If you plan to make your Wear OS apps available for China, see Create Wear OS apps for China.
Create a Wear OS app
You can create a Wear OS app using Android Studio's New Project wizard.
Start a Wear OS project
To create a project in Android Studio:
- Click File > New > New Project.
- In the Project Template window, click the Wear OS tab, select Blank Activity, and click Next.
-
In the New Project window, name your project, fill out the standard project information, and click Finish.
Android Studio creates a project with an app module for your data provider.
- In the
build.gradlefile for the app module:- In the
androidsection, confirm that thecompileSdkVersionis set to 28. - In the
androidsection, confirm that thetargetSdkVersionis set to 28. - Replace the
dependenciessection with Wear OS specific dependencies.
- In the
- In the Android Manifest file, ensure the
<uses-feature>tag is defined. Defineandroid:name="android.hardware.type.watch"as shown in the following example:<manifest> ... <uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.type.watch" /> ... </manifest>
- Sync your Android Studio project. To run the code in the new module, see Launch the emulator and run your Wear OS app.
Launch the emulator and run your Wear OS app
To use the emulator, configure an Android Virtual Device (AVD). Confirm that you have the latest version of the Android SDK Platform-tools from the SDK Manager.
Configure an AVD and run your app as follows:
- In Android Studio, open the Android Virtual Device Manager by selecting Tools > AVD Manager.
- Click Create Virtual Device.
- In the Category pane, select Wear OS and choose a hardware profile. Click Next.
- Select a system image to download. For example, select the image with the Release Name Pie, API Level 28, and the Target "Android 9.0 (Wear OS)". Click Next and then click Finish.
- Close the Android Virtual Device Manager.
- In the Android Studio toolbar, select the AVD you just created from the target device drop-down menu, then click Run
 .
. The AVD starts and, after a few moments, runs your app. A "Hello..." message is displayed.
For more information about using AVDs, see Run apps on the Android Emulator.
Update a Wear OS project
If you have an existing project, you may need to update your settings.gradle file. Make sure you use google() to indicate the Google Maven repository. For related information, see Google's Maven repository.
Your settings.gradle file for your Android Studio project should include this:
dependencyResolutionManagement { ... repositories { google() jcenter() } } Warning: The JCenter repository became read-only on March 31st, 2021. For more information, see JCenter service update.
Set up a watch
Deploying an app to a watch is similar to deploying an app to a phone.
This section assumes that your watch has a USB port. If your watch lacks a USB port, see the instructions for connecting your watch using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
Enable adb debugging on the watch:
- Open the Settings menu on the watch.
- Scroll to the bottom of the menu. If no Developer options item is provided, tap System and then About.
- Tap the build number 7 times.
- From the Settings menu, tap Developer options.
- Enable ADB debugging.
Connect the watch:
- Connect the watch to your machine through USB, so you can install apps directly to the watch.
- On the watch, tap Always allow from this computer and tap OK.
After you connect the watch, run your app by selecting a deployment target as described in Build and run your app.
Set up a phone
This section contains information about setting up a companion phone with a Wear OS companion app.
Note: Wear OS apps should be standalone, and work independently of a phone. However, if your app depends on a phone app, see the following information about updating a phone with the latest Wear OS companion app.
Use the Android version of the companion app
On an Android phone, go to the Wear OS app listing. Tap Update to download and install the app. After installation, confirm that Auto-update is selected for the app (see the "Set up automatic updates for specific apps" section of Update downloaded apps). Tap Open to start the app.
Pair an Android phone to a watch
After you install the companion app on a phone, unpair any obsolete watch pairings, if necessary. Then pair the phone to a newly-imaged watch:
- On the phone, select your device name from the list of devices. A pairing code is displayed on the phone and on the watch. Ensure that the codes match.
- Tap Pair to continue the pairing process. When the watch is connected to the phone, a confirmation message is displayed. On the phone, a screen is displayed that lists the accounts on the phone.
- Choose a Google Account to add and sync to your watch.
- Confirm the screen lock and enter the password to start the copying of the account from the phone to the watch.
- Follow the instructions in the wizard to finish the pairing process.
Companion app for iPhones
An iOS companion app is available but the phone on which the app is installed must be running iOS 8.2 or higher:
- On your iPhone, visit the App Store and download and install the Wear OS companion app on your iPhone.
- Follow the instructions on the watch and on the phone to begin the pairing process. For additional information, see the related Help page.
Pair devices with a watch emulator
You can pair devices to your watch Android Virtual Device (AVD), or emulator, manually or by using the Wear OS emulator pairing assistant.
Use the Wear OS emulator pairing assistant
Note: Your phone must run Android 11 (API level 30) or higher and have the Google Play Store installed to use the Wear OS emulator pairing assistant. Also, make sure your Wear emulators run API level 28 or higher to use the latest assistant features. To upgrade system images for your emulated devices, use the SDK Manager.
The Wear OS emulator pairing assistant makes it easier to manage and connect Wear emulators. You can pair multiple Wear devices with a single virtual or physical phone; Android Studio also remembers and re-pairs previously paired devices when they're launched.
To pair two devices, follow these steps:
- If you haven't already, create a Wear emulator.
-
In the Device Manager, press the "overflow" dropdown menu icon of one of the devices you want to pair and select Pair Wearable.
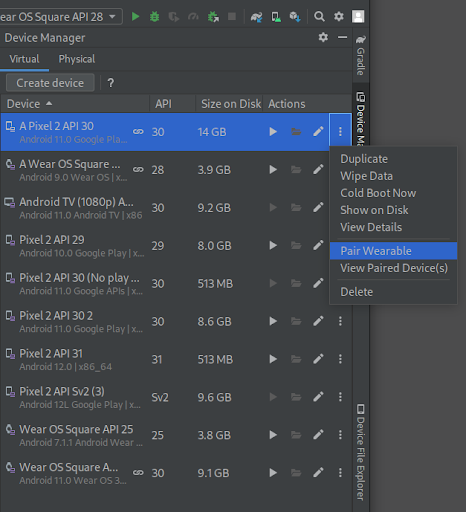
Figure 1. Dropdown menu of a device that can be paired with a Wear emulator. - This launches the Wear OS emulator pairing assistant. If you clicked Pair Wearable on a phone, you see a list of available Wear devices. If you started with a Wear device, you see a list of available phones. Select the device you want to pair, and click Next.
- It might take a few minutes for Android Studio to launch and prepare the devices. If your phone doesn't have the Wear OS companion app installed already, follow the prompts to login to the Play Store, install it, and set it up.
- To pair your devices in the Wear OS app on your phone, click the three dot menu and select Pair with emulator.
After your devices are successfully paired, the Device Manager shows small icons next to the paired devices. You can also click on the overflow dropdown menu and select View Details to see a list of paired devices.
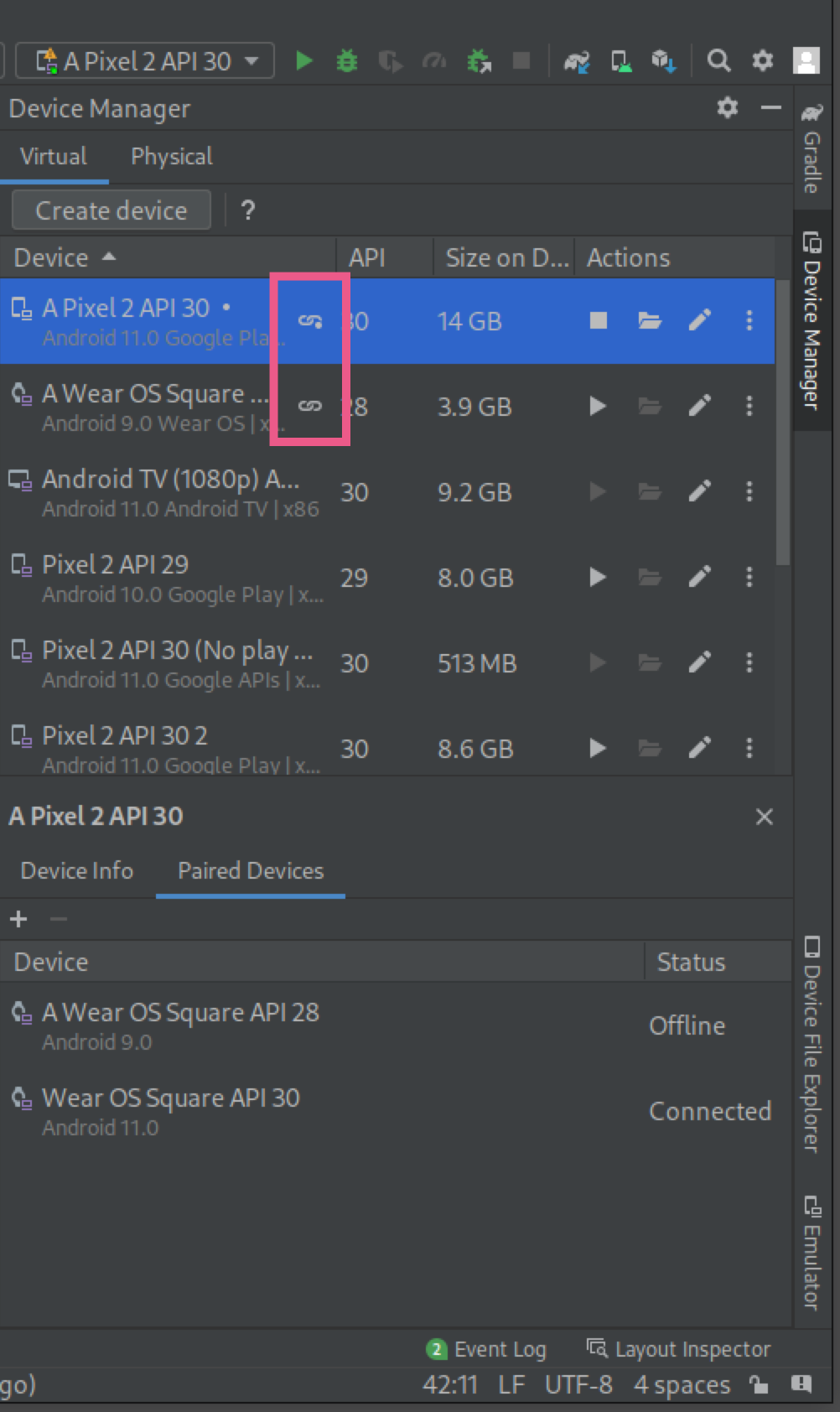
Pair a phone with the watch AVD
If you want a Google Account on the watch AVD for development, you can pair a phone with the watch AVD and sync a Google Account:
- Follow the steps to set up a phone.
- On the phone, enable Developer Options and USB Debugging.
- Connect the phone to your computer through USB.
- Forward the AVD's communication port to the connected phone (each time the phone is connected):
adb -d forward tcp:5601 tcp:5601 - On the phone, in the Wear OS app, begin the standard pairing process. For example, on the Welcome screen, tap the Set It Up button. Alternatively, if an existing watch already is paired, in the upper-left drop-down, tap Add a New Watch.
- On the phone, in the Wear OS app, tap the Overflow button, and then tap Pair with Emulator.
- Tap the Settings icon.
- Under Device Settings, tap Emulator.
- Tap Accounts and select a Google Account, and follow the steps in the wizard to sync the account with the emulator. If necessary, type the screen-lock device password, and Google Account password, to start the account sync.
Connect a phone to multiple Wear devices
To connect a second Wear device to a virtual or physical phone, follow the same steps you would for an initial pairing: locate the phone or Wear device you want to pair in the Device Manager, click on the overflow dropdown menu, and click Pair Wearable.
Add a Wear OS module to your project
You can add a module for a Wear OS device to your existing project in Android Studio, enabling you to reuse code from your mobile (phone) app.
Provide a Wear OS module in your existing project
To create a Wear OS module, open your existing Android Studio project and do the following:
- Click File > New > New Module.
- In the New Module window, select Wear OS Module and click Next.
- Under Configure the new module, enter:
- Application/Library Name: This string is the title of your app launcher icon for the new module.
- Module Name: This string is the name of the folder for your source code and resource files.
- Package Name: This string is the Java namespace for the code in your module. The string is added as the
packageattribute in the module's Android manifest file. - Minimum SDK: Select the lowest version of the platform that the app module supports. For example, select API 26: Android 8.0. This value sets the
minSdkVersionattribute in thebuild.gradlefile, which you can edit later.
- Click Next. You will see multiple code template options. Click Blank Wear OS Activity and click Next.
- In the Configure Activity window, enter or accept the default values for the Activity Name, Layout Name, and Source Language. Click Finish.
Android Studio creates and syncs the files for the new module. Android Studio also adds any required dependencies for Wear OS to the new module's build file. The new module appears in the Project window on the left side of the screen. If you don't see the new module's folder, ensure the window is displaying the Android view.
Include the following in the build.gradle file for the new Wear OS module:
- In the
androidsection, set the values forcompileSdkVersionandtargetSdkVersionto 28. - Add the dependencies you need. For more information, see Declaring dependencies.
- Sync your Android Studio project. To run the code in the new module, see Launch the emulator and run your Wear OS app.
Include libraries
Note: We recommend using Android Studio for Wear OS development, as it provides project setup, library inclusion, and packaging.
When you use Android Studio's Project Wizard, the wizard imports dependencies in the appropriate module's build.gradle file. However, the dependencies are not required for all apps; please review the information below about the dependencies.
To update an existing Wear OS project to the latest SDK version, use the settings listed in the Start a Wear OS project section.
Notifications
For information about dependencies for notifications, see Create a notification on Wear.
Wear OS UI Library
The components in the Wear OS UI Library are recommended because they exemplify best practices for watch apps. Therefore, it is recommended that you add a dependency on the Wear OS UI Library. For more information, see the following pages:
- Using the Wear OS UI Library
- Create custom layouts
- Reference documentation:
-
androidx.wear.ambient -
androidx.wear.input -
androidx.wear.widget -
androidx.wear.widget.drawer
-
Other Jetpack libraries
Wear OS has been migrating away from the support library to Jetpack. A full list of all the new classes is in our release notes. Here are some of the highlights:
-
androidx.wear -
wear-ongoing -
wear-phone-interactions -
wear-remote-interactions -
wear-tiles
Play Services and the Wearable Data Layer APIs
If your app depends on Google Play Services, either to sync and send data (using the Data Layer APIs) or for other reasons, you need the latest version of Google Play Services. If you are not using these APIs, remove the dependency.
Differences between phone and watch apps
The following are some of the differences between phone and watch apps:
- Watch apps use watch-specific APIs, where applicable (e.g., for circular layouts, wearable drawers, ambient mode, etc.).
- Watch apps have a different UX model.
- Watch apps contain functionality appropriate to a watch.
-
Watch apps can access many standard Android APIs, but don't support the following:
-
android.webkit -
android.print -
android.app.backup -
android.appwidget -
android.hardware.usb
You can check if a watch supports a feature by calling
hasSystemFeature()before using an API. -
Save power on the watch
A watch transitions from interactive mode to ambient mode when the watch is idle or when a user covers the screen with their palm.
To conserve power on a watch, avoid using ambient mode. If the watch goes into the system ambient mode while your app is active and the user interacts again with their watch within a specified amount of time, your app will be brought up as the first thing they see.
You may want to override ambient mode in your app for specific use cases. For example, override ambient mode if the user is tracking a run and needs to see the time at all times.
Watch apps that can transition into ambient mode are called always-on apps. The following describes the two modes of operation for always-on apps:
- Interactive
- Use full color with fluid animation in this mode. The app is also responsive to input.
- Ambient
- Render the screen with black and white graphics and do not present any input cues in this mode. This display mode is only supported on devices running Android 5.1 or higher.
For more information and best practices, review the Keep your app visible on Wear OS page.
buckwalterstany1979.blogspot.com
Source: https://developer.android.com/training/wearables/get-started/creating
0 Response to "Continue on Phone Android Wear Update"
Post a Comment